'Product Blog'
Novel High Surface Area Silica Nanoparticles
A New Family of Silica Nanospheres is Improving the Activities of Catalytic Reactions
Novel fibrous shaped silica nanospheres, denoted as KCC-1 (KAUST Catalysis Center),[1] have unique physical properties which have never before been reported in silica materials. These nanomaterials have been developed by Prof. J. M. Basset of King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST). A fibrous surface morphology arranged in three-dimensional structure forms the spheres (Fig. 1). Unlike traditional pore-based silica, these nanospheres possess a fibrous structure that increases accessibility of the available surface area; this in turn, significantly increases the catalytic activity.
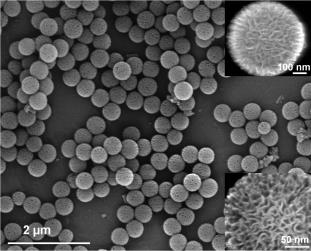
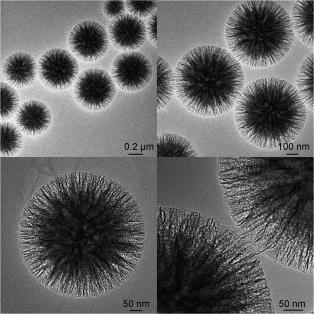
Figure 1. SEM and HRTEM images of silica nanospheres KCC-1
These materials exhibit excellent physical properties, including a high surface area, a fibrous surface morphology, good thermal and hydrothermal stabilities and high mechanical stability (Table 1). The fibrous morphology of KCC-1 remains unaffected even after mechanical compression up to 216 MPa pressure. This is superior compared to the conventional MCM-41 type of silica, which is affected at a pressure of 86 MPa.[1]
|
Product # |
Category |
Grade |
particle size |
surface area |
Pore Volume |
|
14-6100 |
Large |
(KCC-1 L1) |
~900-1000 |
~700 |
~1.4 |
|
14-6110 |
Large |
(KCC-1 L2) |
~900-1000 |
~600 |
~1.2 |
|
14-6120 |
Large |
(KCC-1 L3) |
~900-1000 |
~550 |
~0.9 |
|
14-6200 |
Medium |
(KCC-1 M1) |
~400-450 |
~400 |
~0.7 |
|
14-6210 |
Medium |
(KCC-1 M2) |
~300-350 |
~600 |
~0.6 |
|
14-6300 |
Small |
(KCC-1 S1) |
~130-190 |
~380 |
~1.7 |
Table.1: Summary of properties of KCC-1 product portfolio
A range of heterogeneous catalysts, prepared using KCC-1 as a supporting material, have been showing excellent catalytic activity for various transformations of research and industrial importance. As a catalyst support, sorbent or carrier, KCC-1 is able to demonstrate superior activity as compared to regular mesoporous silica materials in energy related processes,[2-3] a variety of organic reactions,[4-7] biomedical applications and drug delivery systems [8], optoelectronic devices [9] and many others.
References:
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9652.
- Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8237.
- ACS Catalysis. 2016, 6, 2770.
- ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 85.
- Green Chem., 2016, 18, 5890.
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2747.
- RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 24885.
- Langmuir 2014, 30, 10886.
- J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015, 3, 3201.
Items mentioned in this blog:
To download our literature sheet for these items please visit the link below:
High Surface Area Silica Nanoparticles