'Product Blog'
A Scandium Source for ALD of Thin Film Oxides
Scandium Formamidinate is a Promising ALD Precursor for High-k Oxide Dielectrics
As microelectronic devices continue to scale down in size, high quality dielectric films are required to improve transistor performance. It is now necessary to incorporate greater dielectric constant materials to eliminate the high gate leakage experienced by ultrathin films in metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) devices. Scandium oxide (21-2112) is a high-k oxide material that has been reported as a promising dielectric on GaN-based transistors (HEMT’s).1 Ternary rare-earth oxides have also drawn interest as possible candidates for next generation high-k materials. Among these oxides showing desirable growth results by Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), are thin films of lanthanum scandate (LaScO3) and gadolinium scandate (GdScO3). The advantages of using the ALD process to grow these gate dielectrics include: excellent film uniformity over large areas, high conformality for aggressive device geometries, the ability to adapt to large-scale production and most importantly, the ability of depositing films with minimal thickness while maintaining their desirable electrical and structural properties. Both LaScO3 and GdScO3 films can be deposited by ALD with minimal interlayer thickness and retain the desirable high-k and amorphous properties. 2,3
A new Scandium precursor, Tris(N,N’-di-i-propylformamidinato)scandium(III) (21-1200) is now available for the ALD deposition of high quality oxide and ternary oxide thin films. Advantages of using amidinate ligand-metal bonds in Sc precursor chemistry are inherent thermal stability, suitable volatility and the thermodynamic driving force when reacted with water for breaking nitrogen bonds and forming oxygen bonds.4 Deposited by ALD, this amidinate precursor possesses high reactivity to water and results in metal oxide films with volatile amidine byproducts.
Catalog #21-1200 Tris(N,N’-di-i-propylformamidinato)scandium(III), (99.9%-Sc)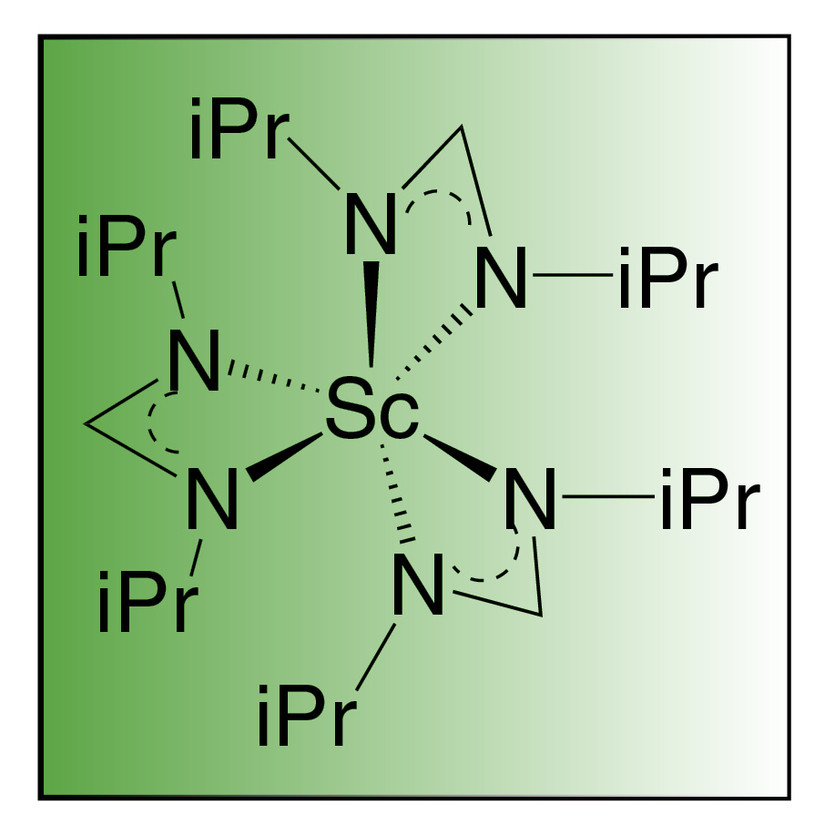
References:
1. Xinwei Wang, Omair I. Saadat, Bin Xi, Xiabing Lou, Richard J. Molnar, Tomas Palacios and Roy G. Gordon., Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101, 232109
2. Kyoung H. Kim, Damon B. Farmer, Jean-Sebastien M. Lehn, P. Venkateswara Rao and Roy G. Gordon, Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89, 133512
3. Hongtao Wang, Jun-Jieh Wang, Roy Gordon, Jean-Sébastien M. Lehn, Huazhi Li, Daewon Hong and Deo V. Shenai, Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2009, 12 (4), G13-G15.
4. Philippe de Rouffignac, Andrew P. Yousef, Kyoung H. Kim, and Roy G. Gordon, Electrochemical and Solid- State Letters, 2006, 9 (6), F45-F48.
Products mentioned in this blog and related products:
21-1200: Tris(N,N'-di-i-propylformamidinato)scandium(III), (99.9%-Sc)
21-2112: Scandium(III) oxide (99.99%-Sc) (REO) PURATREM [12060-08-1]
93-2113: Scandium(III) oxide (99.9%-Sc) (REO) [12060-08-1]
21-0750: Scandium(III) oxide, sintered lumps (99.9%-Sc) (REO) [12060-08-1]
57-1200: Tris(N,N'-di-i-propylformamidinato)lanthanum(III), (99.999+%-La) PURATREM La-FMD [1034537-36-4]
Additional Resources:
Full Line of High Purity CVD/ALD Precursors
CVD/ALD Precursors contained in Swagelok® Cylinders
Cylinder and Adaptors
Metal Amidinates for CVD/ALD Applications
MOCVD, CVD & ALD Precursors Booklet
Stainless Steel Bubblers: Vertical Electropolished